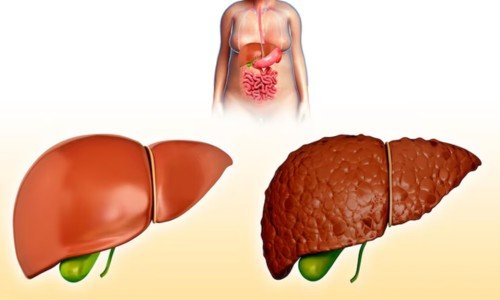
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty Liver Disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, occurs when excess fat builds up in the liver. This condition can progress to more serious liver damage if not managed properly. There are two main types: Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD).
Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty Liver Disease often shows no symptoms in its early stages, but as the condition progresses, patients may experience:
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy.
- Abdominal Discomfort: Mild pain or a sense of fullness in the upper right abdomen.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss in advanced stages.
- Weakness: General feeling of being unwell.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, indicating severe liver damage.
- Swelling: In the abdomen and legs due to fluid accumulation (edema).
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of Fatty Liver Disease differ between NAFLD and AFLD, but common risk factors include:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):
- Obesity: Excess body weight is a significant risk factor.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin resistance is closely linked to NAFLD.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of lipids in the blood.
- Metabolic Syndrome: A combination of conditions, including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- Poor Diet: High intake of refined carbohydrates and sugary beverages.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD):
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Chronic heavy drinking leads to fat accumulation in the liver.
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history of liver disease or alcoholism.
- Malnutrition: Poor dietary habits associated with alcohol abuse.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
At Adithya Gastro and Liver Care Clinic in Manikonda, Hyderabad, Dr. G Harsha Vardhan Reddy uses advanced diagnostic tools to identify Fatty Liver Disease:
- Medical History and Physical Exam: Comprehensive review of symptoms, lifestyle factors, and physical examination.
- Blood Tests: To check liver function and identify markers of liver inflammation or damage.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize fat accumulation in the liver.
- Liver Biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of liver tissue is examined under a microscope to assess the extent of liver damage and rule out other conditions.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Weight Loss: Gradual weight loss through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Healthy Diet: Emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while avoiding sugary drinks, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity most days of the week.
- Alcohol Abstinence: Complete avoidance of alcohol in cases of AFLD.
Medications:
- Insulin Sensitizers: Such as metformin to improve insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes.
- Lipid-Lowering Agents: Statins to manage high cholesterol levels.
- Vitamin E: In certain cases, vitamin E supplements may help reduce liver inflammation.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: Regular check-ups and liver function tests to monitor disease progression and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
Why Choose Adithya Gastro and Liver Care Clinic?
Dr. G Harsha Vardhan Reddy and his team at Adithya Gastro and Liver Care Clinic are dedicated to providing comprehensive care for patients with Fatty Liver Disease. With a focus on personalized treatment plans and preventive strategies, we aim to help patients achieve and maintain optimal liver health.